What is Urticaria on the Skin? Understanding Hives, Causes, and Treatments
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the body. These welts, or wheals, vary in size and shape and often come and go. Understanding what is urticaria on the skin is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and various treatment options available for urticaria.
Understanding Urticaria: The Basics
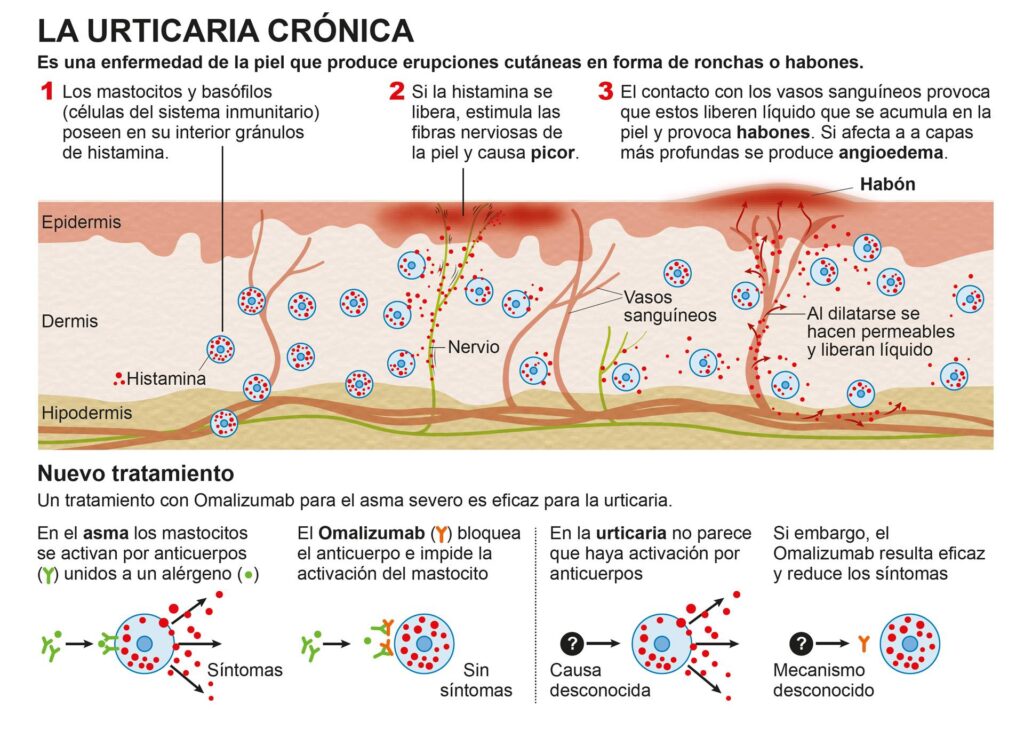
What is urticaria on the skin, exactly? Urticaria arises from the release of histamine and other chemicals in the skin, causing small blood vessels to leak fluid. This fluid accumulates in the skin, resulting in the characteristic raised welts. These welts can be intensely itchy and often surrounded by a red flare. Urticaria can be acute, lasting less than six weeks, or chronic, persisting for longer periods. Acute urticaria is often triggered by allergies, while chronic urticaria can be more complex and may not always have an identifiable cause.
Acute vs. Chronic Urticaria
The duration of urticaria is a key factor in its classification. Acute urticaria typically resolves within a few days to weeks and is often associated with a specific trigger, such as a food allergy or medication. Chronic urticaria, on the other hand, lasts for more than six weeks and can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Identifying the underlying cause of chronic urticaria can be challenging, and treatment often focuses on managing symptoms.
Causes of Urticaria
Several factors can trigger urticaria on the skin. These triggers vary from person to person, making it essential to identify individual sensitivities. Common causes include:
- Allergies: Food allergies (e.g., nuts, shellfish, eggs), insect stings, and exposure to allergens like pollen or pet dander.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics (penicillin), NSAIDs (ibuprofen), and ACE inhibitors.
- Infections: Viral infections (e.g., common cold, influenza), bacterial infections (e.g., strep throat), and fungal infections.
- Physical Stimuli: Pressure, cold, heat, sunlight, or exercise can trigger urticaria in some individuals. This is known as physical urticaria.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: In some cases, urticaria can be associated with underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis) or thyroid disorders.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate urticaria in susceptible individuals.
Symptoms of Urticaria
The primary symptom of urticaria on the skin is the presence of raised, itchy welts. These welts can vary in size, shape, and location on the body. Other symptoms may include:
- Itching: Intense itching is a hallmark of urticaria.
- Welts: Raised, red or skin-colored welts that can appear and disappear rapidly.
- Angioedema: Swelling of the deeper layers of the skin, often affecting the face, lips, tongue, and throat. Angioedema can be life-threatening if it affects breathing.
- Burning or Stinging Sensation: Some individuals may experience a burning or stinging sensation in addition to itching.
Recognizing Angioedema
Angioedema is a related condition that often accompanies urticaria. It involves swelling in the deeper layers of the skin, particularly around the eyes, lips, and throat. Angioedema can be dangerous if it affects the airway, causing difficulty breathing. Immediate medical attention is necessary if angioedema occurs.
Diagnosing Urticaria
Diagnosing what is urticaria on the skin typically involves a physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. The doctor will ask about potential triggers, medications, and any underlying medical conditions. In some cases, allergy testing may be recommended to identify specific allergens. Other diagnostic tests may include:
- Skin Prick Test: A small amount of allergen is applied to the skin, and the skin is pricked to allow the allergen to enter. A positive reaction indicates an allergy.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify underlying medical conditions or elevated levels of certain antibodies that may be contributing to urticaria.
- Physical Urticaria Testing: These tests involve exposing the skin to specific stimuli, such as cold, heat, or pressure, to determine if they trigger urticaria.
Treatment Options for Urticaria
The treatment for urticaria on the skin aims to relieve symptoms and identify and avoid potential triggers. Treatment options may include:
- Antihistamines: These medications block the action of histamine, reducing itching and welts. Non-sedating antihistamines are often the first-line treatment.
- Corticosteroids: In severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. However, these medications are typically used for short-term treatment due to potential side effects.
- H2 Blockers: These medications can help reduce the production of stomach acid, which can sometimes contribute to urticaria.
- Leukotriene Inhibitors: These medications block the action of leukotrienes, which are inflammatory chemicals that can contribute to urticaria.
- Omalizumab: This is an injectable medication that targets IgE, an antibody involved in allergic reactions. It is often used for chronic urticaria that does not respond to other treatments.
- Identifying and Avoiding Triggers: Avoiding known triggers is essential for managing urticaria. This may involve avoiding certain foods, medications, or environmental factors.
Home Remedies for Urticaria
In addition to medical treatments, several home remedies can help relieve symptoms of urticaria on the skin:
- Cool Compresses: Applying cool compresses to the affected area can help reduce itching and inflammation.
- Oatmeal Baths: Oatmeal baths can soothe irritated skin and relieve itching.
- Loose Clothing: Wearing loose, comfortable clothing can help prevent further irritation of the skin.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid harsh soaps, detergents, and lotions that can irritate the skin.
Living with Chronic Urticaria
Living with chronic urticaria on the skin can be challenging. The constant itching and welts can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. However, with proper management and treatment, individuals can learn to cope with the condition and minimize its impact.
Tips for Managing Chronic Urticaria
- Keep a Diary: Keep a diary to track potential triggers and symptoms. This can help identify patterns and potential causes of urticaria.
- Avoid Known Triggers: Avoiding known triggers is essential for managing chronic urticaria.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate urticaria. Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Follow Your Doctor’s Recommendations: Follow your doctor’s recommendations for medication and lifestyle changes.
- Join a Support Group: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and connect you with others who understand what you are going through.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of urticaria on the skin are mild and resolve on their own, it is essential to seek medical attention if:
- Symptoms are severe or interfere with daily activities.
- Angioedema occurs, especially if it affects breathing.
- Urticaria is accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, joint pain, or abdominal pain.
- Symptoms persist for more than a few days.
Conclusion
Understanding what is urticaria on the skin, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. While urticaria can be uncomfortable and frustrating, most cases can be successfully treated with medication and lifestyle changes. Identifying and avoiding triggers, managing stress, and following your doctor’s recommendations are essential for living with chronic urticaria. If you experience severe symptoms or angioedema, seek immediate medical attention. Urticaria can stem from a variety of sources, so thorough investigation is key to relief. [See also: Managing Skin Allergies] and [See also: Understanding Autoimmune Diseases]. Remember that knowing what is urticaria on the skin and how to manage it is empowering. With careful management, you can minimize the impact of urticaria on the skin and maintain a good quality of life. Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional to get personalized advice on what is urticaria on the skin and the best course of treatment for you. Urticaria on the skin can be challenging, but with knowledge and proactive care, it can be effectively managed. Knowing what is urticaria on the skin is the first step towards relief and improved quality of life. Managing urticaria on the skin requires a holistic approach, including medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Understanding what is urticaria on the skin helps in making informed decisions about treatment and prevention. Early diagnosis and intervention are key when dealing with urticaria on the skin. If you’re dealing with urticaria on the skin, remember that you’re not alone, and effective treatments are available. Therefore, seek medical advice to understand what is urticaria on the skin and how you can manage it effectively.
